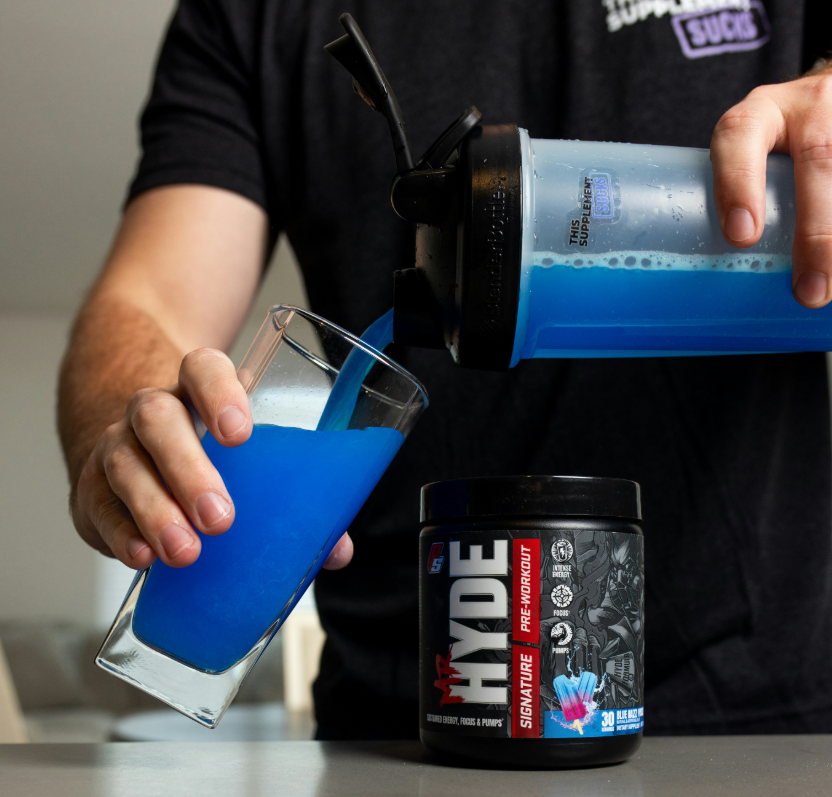
- MIXES FLAWLESSLY – More pumps, and no clumps. Unlike traditional Glycerol Powders, HydroPrime is a much more stable, bre…
- 5,000 MG GLYCEROL – By adding Glycerol to your pre-workout, you can hold upwards of an extra liter of water via intramus…
- IMPROVED ENDURANCE – Sufficient water intake coupled with the supplementation of glycerol has been shown to lower heart …
Understanding Intramuscular Hyper-Hydration
Intramuscular hyper-hydration is a physiological condition characterized by an increased volume of fluid stored within muscle cells. This state is achieved when the muscles are saturated with water beyond their normal hydration levels, resulting in significantly larger and fuller muscle appearance, commonly referred to as “muscle pumps.” This phenomenon is not just aesthetic; it plays a crucial role in enhancing athletic performance, particularly for bodybuilders and athletes aiming to maximize strength and endurance during intense workouts.
The process of intramuscular hyper-hydration involves several physiological mechanisms. Firstly, when individuals consume water or hydrating agents, it leads to an osmotic gradient that encourages water retention within the muscle cells. This influx of fluid increases cell volume, which can positively affect muscle contractility and energy production. The enhanced hydration status assists in facilitating metabolic reactions, thus providing muscles with the necessary resources for prolonged performance and recovery.
The transition from typical hydration practices to intramuscular hyper-hydration marks a significant difference in how athletes approach their hydration strategies. Traditional hydration primarily focuses on overall body fluid balance, which involves drinking water or electrolyte solutions to prevent dehydration. In contrast, intramuscular hyper-hydration emphasizes the deliberate accumulation of water within muscle cells to optimize muscle function and promotes enhanced blood flow during workouts. This targeted approach not only improves muscle endurance but also contributes to reduced fatigue levels, enabling athletes to perform at a higher intensity for extended periods.
Incorporating strategies for intramuscular hyper-hydration can lead to marked improvements in performance, making it an essential consideration for those committed to pushing their physical limits. The benefits of this hydration strategy are profound, elevating the workout experience while fostering long-term gains in strength and muscle mass.
Key Ingredients for Intense Pumps
Achieving intramuscular hyper-hydration is significantly influenced by specific key ingredients that aid in muscle cell volumization. Among the most recognized supplements are creatine, glycerol, and citrulline malate. Each of these ingredients plays a crucial role in enhancing muscle pumps, thereby improving overall athletic performance.
Creatine is perhaps the most studied and widely utilized supplement in the fitness world. It serves as a high-energy phosphate donor, primarily in muscle tissues, facilitating the rapid regeneration of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—the energy currency of the cell. This process leads to enhanced muscular contractions and increased performance in high-intensity exercises. For optimal results, a common recommendation is to supplement with 3 to 5 grams of creatine daily, ideally consumed after workouts to maximize uptake and effects.
Glycerol, on the other hand, acts as a hyper-hydrating agent, promoting the retention of water within muscle cells. It facilitates a phenomenon known as cellular hydration, which can significantly enhance the volume and appearance of muscles during workouts. The recommended dosage for glycerol typically ranges from 1 to 2 grams, consumed alongside water before exercise. This practice helps in achieving a sufficient level of hydration, crucial for maximizing performance and intensity.
Another powerful ingredient is citrulline malate, which is known for its role in increasing nitric oxide levels in the body. This increase leads to enhanced blood flow to the muscles, causing improved nutrient delivery during exercise. When taken in doses between 6 to 8 grams approximately 30–60 minutes before a workout, citrulline malate can effectively boost pump and endurance by reducing muscle soreness post-exercise.
Creating the Perfect Formula for Hyper-Hydration
Formulating a supplement regime that enhances intramuscular hyper-hydration requires careful consideration of various key ingredients and individual goals. To commence this process, it is essential to identify which specific ingredients will serve your hydration needs best. Common components known for their role in hyper-hydration include creatine, amino acids, electrolytes, and carbohydrates. Each of these plays a significant part in cellular hydration, thus contributing to the enhanced volumization of muscle cells.
When determining the form of supplements to use, both powders and capsules have distinct advantages. Powders can provide quick absorption and allow for flexible dosing, which is particularly beneficial for individuals aiming for precise intake tailored to workout intensity. Conversely, capsules offer convenience and portability, making them an appealing choice for those on the go. However, it is important to assess one’s preferred method of consumption whilst ensuring compatibility with the selected ingredients to achieve optimal results.
Individual goals significantly influence the formulation process. For instance, an athlete aiming for peak performance may prioritize quick absorption of electrolytes and carbohydrates, while someone focused on muscle recovery may benefit more from incorporating amino acids or creatine. Personal dietary restrictions and lifestyle choices should also factor into the equation, ensuring that the selected supplements do not interact negatively with other components of your diet.
Lastly, proper hydration and a balanced diet are crucial in maximizing the effectiveness of any hyper-hydration formula. Ensuring an adequate intake of fluid throughout the day creates a foundation that enhances the impact of the supplements. In synergy with a nutritious diet, this strategy will create a comprehensive regimen tailored to achieving the desired intensity of intramuscular hyper-hydration.
Best Practices for Achieving Intense Muscle Pumps
To achieve intense muscle pumps, implementing effective techniques and adhering to a structured regimen is essential. One of the primary components is optimizing the timing of supplementation. Consuming hyper-hydration supplements approximately 30 to 60 minutes before your workout can significantly enhance vascularity and fluid retention within the muscle cells. Products containing ingredients such as creatine, citrulline, and electrolytes can play a vital role in this process, promoting pump effects and providing sustained energy levels during intense training sessions.
Moreover, it is crucial to employ strategies that intensify workouts. Focus on compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses, as these movements recruit multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Incorporating techniques such as drop sets and supersets will maximize time under tension, thereby increasing the pump. Additionally, maintaining a controlled tempo—especially during the eccentric phase—can further elevate the intramuscular pressure, leading to heightened muscle swelling.
Equally important are the warm-ups and cool-downs associated with training. A proper warm-up increases blood flow to the muscles and prepares the body for exertion. Dynamic stretches and mobility drills can be beneficial in this regard, ensuring that muscles are receptive to the hyper-hydration process. Conversely, cooling down after a workout aids recovery and reduces muscle soreness, balancing the pump gained with the potential for overtraining.
Despite the various strategies available, recognize that individual responses to supplements and training methods can vary. Factors such as genetics, fitness level, and nutritional habits can influence your results. It’s vital to monitor your progress and adjust your approach as necessary, avoiding common pitfalls like over-reliance on supplements or neglecting foundational training principles. With dedication and the right practices, achieving intense muscle pumps is not only possible but can become a fundamental aspect of your fitness journey.